Probably the best-known use of a torsion spring is the torsion bar, a torsion bar spring invented by Ferdinand Porsche and patented by him in 1931. Since then, the torsion bar has been used as a cost-effective spring element, particularly in automotive engineering. In addition to this type of use, torsion springs can also be found in industrial and plant engineering and provide reliable service in millions of garage doors. A look at a classic technical spring.
What is a torsion spring?
The name torsion spring comes from the required property that these springs must fulfil. Technical spring must fulfil. Twisting means "twisting" or "warping".
A torsion spring is therefore a type of spring that is used to perform a continuous rotational movement. The Torsion refers to the twisting or twisting of a body. When a body is twisted (torqued), this moment is referred to as the torsional moment. If you take a rod and try to twist it with a lever perpendicular to the longitudinal axis, a torsional moment acts on it.
How do torsion springs work?
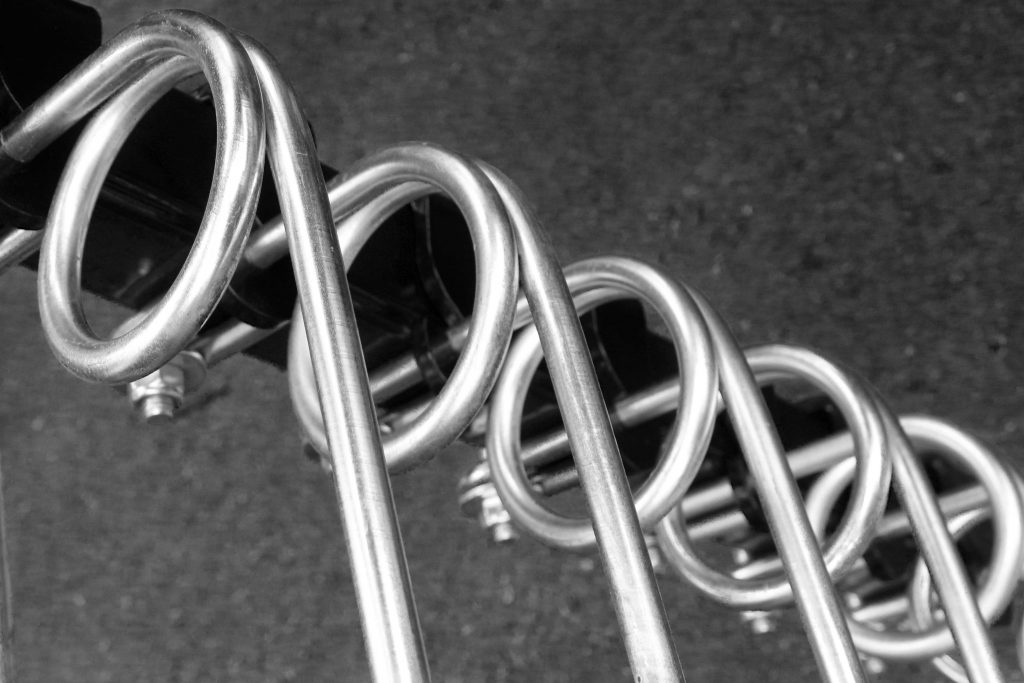
As a rule, there are Torsion springs made from strips, rods or wires with a round cross-section. When in use, they perform permanent rotational movements. The outer sides of the torsion springs are attached to a component. These two sides then perform the rotating or swivelling movement against each other. This results in Twisting of the body axes. The torsional moment mentioned above.
Torsion spring calculation
The wide range of applications for these spring designs requires precise configuration and torsion spring calculation for spring production.
The spring rate (also spring constant) describes the torsional stress. Wire thickness, angle of rotation, torque, mandrel diameter, coil diameter, coil direction and many other criteria must be calculated precisely. There are many parameters that are decisive in the production of torsion springs.
The material and the basic shape of the spring make a general difference. In addition to straight torsion springs, which are Rod or torsion bar springs are also available as Coil springscharacterised by their sinuous shape.
Torsion spring Application
Torsion springs are usually used where torque is generated or rotational energy is to be collected. For example, torsion springs are used for hinges, counterweights and lever retractions.
The different areas of application in industrial and plant engineering, but also in the automotive industry, require different spring designs.
Torsion spring versions
Rod or torsion bar springs
As the name suggests, the rod spring has an elongated, rod-shaped structure. Shear stress occurs as soon as this rod is twisted around its longitudinal axis. Important for the calculation of the torsion spring: The shear stress increases with the cross-sectional radius and is proportional to the torsional moment. The shear stress distribution is rotationally symmetrical in the cross-section of the bar.
Rod springs are used as stabilisers for vehicle suspension as well as torsion pendulums in mechanical clocks and torsion bands in moving-coil measuring instruments.
Coil springs
They are wound from spring steel wire in the shape of a coil. "Tension" or "compression" are functions that generally distinguish coil springs:
Extension springs
According to their designation, tension springs are pulled apart. Extension springs are cylindrical spiral springs that store energy, which is utilised by pulling force.
Compression springs
Compression springs, on the other hand, are compressed. Compression springs are cylindrical spiral springs that offer resistance to an applied pressure.
Difference between rod springs and coil springs
A decisive difference between rod springs and coil springs is the stress distribution. With coil springs, the stress distribution is not rotationally symmetrical. As the stress of the concave edge fibres is increased, a correction factor must be applied to compensate for this. This specific torsion spring load is taken into account during production. If the curvature is not treated with heat during production, the permissible stress is reduced.
Torsion springs from the specialist
In today's industrial world, consistent high-tech quality and uncompromising precision are essential. The highest customer demands have therefore become the standard for Schaaf.
We know the dynamics of torsion spring applications. Precision and quality are our top priorities in all tasks. If you are looking for tension springs, compression springs and torsion springs with sustainable and future-oriented characteristics, Schaaf is the right address. Just ask us!













